Gateway
Propósito
Proporcionar una interfaz de acceso a un conjunto de sistemas o funcionalidades externas. Gateway proporciona una vista simple y uniforme de
recursos externos a los internos de una aplicación.
Explicación
Un ejemplo real
Gateway actúa como una verdadera puerta de entrada de una ciudad determinada. Las personas dentro de la ciudad se llaman sistema interno, y las diferentes ciudades externas se llaman servicios externos. La puerta de enlace está aquí para proporcionar acceso al sistema interno a diferentes servicios externos.
En pocas palabras
La pasarela puede proporcionar una interfaz que permita al sistema interno utilizar un servicio externo.
Wikipedia dice
Un servidor que actúa como front-end de la API, recibe solicitudes de la API, aplica políticas de estrangulamiento y seguridad, pasa las solicitudes al servicio back-end y, a continuación, devuelve la respuesta al solicitante.
Ejemplo programático
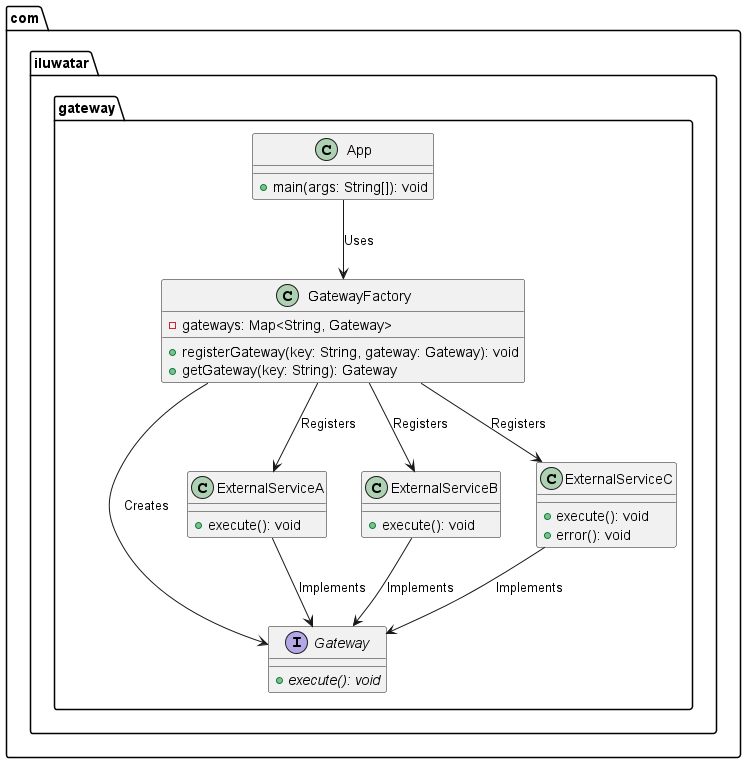
La clase principal de nuestro ejemplo es el ExternalService que contiene elementos.
class ExternalServiceA implements Gateway {
@Override
public void execute() throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("Executing Service A");
// Simulate a time-consuming task
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
/**
* ExternalServiceB is one of external services.
*/
class ExternalServiceB implements Gateway {
@Override
public void execute() throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("Executing Service B");
// Simulate a time-consuming task
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
/**
* ExternalServiceC is one of external services.
*/
class ExternalServiceC implements Gateway {
@Override
public void execute() throws Exception {
LOGGER.info("Executing Service C");
// Simulate a time-consuming task
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
public void error() throws Exception {
// Simulate an exception
throw new RuntimeException("Service C encountered an error");
}
}Para operar estos servicios externos, aquí está la clase App:
public class App {
/**
* Simulate an application calling external services.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
GatewayFactory gatewayFactory = new GatewayFactory();
// Register different gateways
gatewayFactory.registerGateway("ServiceA", new ExternalServiceA());
gatewayFactory.registerGateway("ServiceB", new ExternalServiceB());
gatewayFactory.registerGateway("ServiceC", new ExternalServiceC());
// Use an executor service for asynchronous execution
Gateway serviceA = gatewayFactory.getGateway("ServiceA");
Gateway serviceB = gatewayFactory.getGateway("ServiceB");
Gateway serviceC = gatewayFactory.getGateway("ServiceC");
// Execute external services
try {
serviceA.execute();
serviceB.execute();
serviceC.execute();
} catch (ThreadDeath e) {
LOGGER.info("Interrupted!" + e);
throw e;
}
}
}La interfaz Gateway es extremadamente sencilla.
interface Gateway {
void execute() throws Exception;
}Salida del programa:
Executing Service A
Executing Service B
Executing Service CDiagrama de clases
Aplicabilidad
Utilizar el patrón Gateway
- Para acceder al contenido de un objeto agregado sin exponer su representación interna.
- Para la integración con múltiples servicios externos o APIs.
- Para proporcionar una interfaz uniforme para recorrer diferentes estructuras de agregados.