Business Delegate Pattern in Java: Simplifying Business Service Interaction
Also known as
- Service Representative
Intent of Business Delegate Design Pattern
The Business Delegate pattern is a structural design pattern in Java that adds an abstraction layer between the presentation and business tiers. By using the pattern we gain loose coupling between the tiers and encapsulate knowledge about how to locate, connect to, and interact with the business objects that make up the application.
Detailed Explanation of Business Delegate Pattern with Real-World Examples
Real-world example
In an Enterprise application using Java EE, the Business Delegate pattern helps manage interactions between different business services.
Imagine a restaurant where the waitstaff serves as intermediaries between the customers and the kitchen. When a customer places an order, the waiter takes the order to the kitchen, relays any specific requests, and later brings the prepared food back to the customer. The waitstaff abstracts the complexity of the kitchen operations from the customers, allowing the chefs to focus solely on cooking without needing to interact directly with customers. This setup allows both the customer service (presentation tier) and the kitchen (business service) to operate independently and efficiently. The waitstaff acts as the Business Delegate, managing communication and ensuring smooth interactions between the two distinct areas.
In Plain Words
Business Delegate adds an abstraction layer between the presentation and business tiers.
Wikipedia says
Business Delegate is a Java EE design pattern. This pattern is directing to reduce the coupling in between business services and the connected presentation tier, and to hide the implementation details of services (including lookup and accessibility of EJB architecture). Business Delegates acts as an adaptor to invoke business objects from the presentation tier.
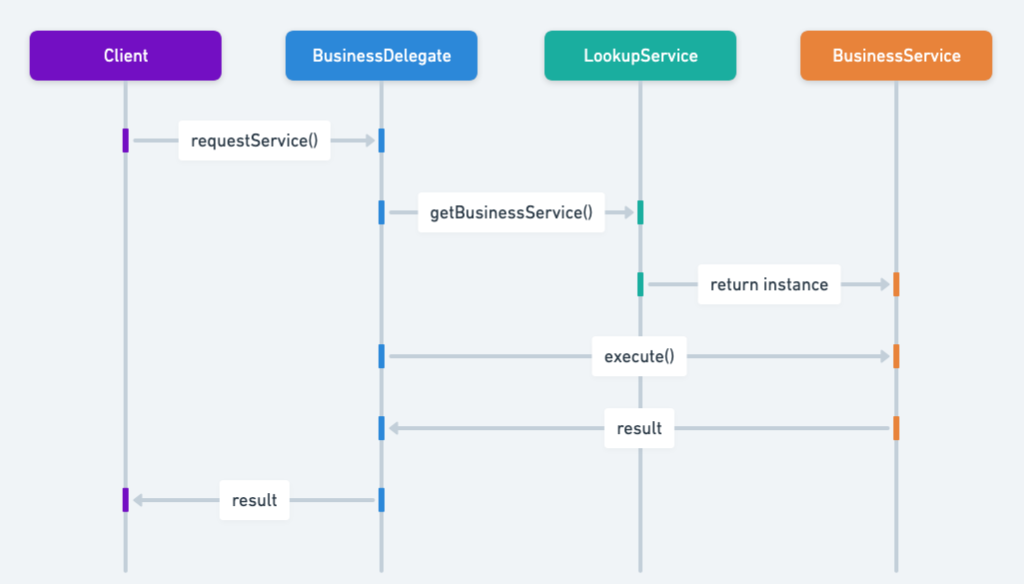
Sequence diagram
Programmatic Example of Business Delegate Pattern in Java
The following Java code demonstrates how to implement the Business Delegate pattern. This pattern is particularly useful in applications requiring loose coupling and efficient service interaction.
A mobile phone application promises to stream any movie in existence to your device. It captures the user's search string and passes this on to the Business Delegate. The Business Delegate selects the most suitable video streaming service and plays the video from there.
First, we have an abstraction for video streaming services and a couple of implementations.
public interface VideoStreamingService {
void doProcessing();
}
@Slf4j
public class NetflixService implements VideoStreamingService {
@Override
public void doProcessing() {
LOGGER.info("NetflixService is now processing");
}
}
@Slf4j
public class YouTubeService implements VideoStreamingService {
@Override
public void doProcessing() {
LOGGER.info("YouTubeService is now processing");
}
}Then, we have a lookup service that decides which video streaming service to use.
@Setter
public class BusinessLookup {
private NetflixService netflixService;
private YouTubeService youTubeService;
public VideoStreamingService getBusinessService(String movie) {
if (movie.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).contains("die hard")) {
return netflixService;
} else {
return youTubeService;
}
}
}The Business Delegate uses a business lookup to route movie playback requests to a suitable video streaming service.
@Setter
public class BusinessDelegate {
private BusinessLookup lookupService;
public void playbackMovie(String movie) {
VideoStreamingService videoStreamingService = lookupService.getBusinessService(movie);
videoStreamingService.doProcessing();
}
}The mobile client utilizes Business Delegate to call the business tier.
public class MobileClient {
private final BusinessDelegate businessDelegate;
public MobileClient(BusinessDelegate businessDelegate) {
this.businessDelegate = businessDelegate;
}
public void playbackMovie(String movie) {
businessDelegate.playbackMovie(movie);
}
}Finally, we can demonstrate the complete example in action.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// prepare the objects
var businessDelegate = new BusinessDelegate();
var businessLookup = new BusinessLookup();
businessLookup.setNetflixService(new NetflixService());
businessLookup.setYouTubeService(new YouTubeService());
businessDelegate.setLookupService(businessLookup);
// create the client and use the business delegate
var client = new MobileClient(businessDelegate);
client.playbackMovie("Die Hard 2");
client.playbackMovie("Maradona: The Greatest Ever");
}Here is the console output.
21:15:33.790 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.business.delegate.NetflixService - NetflixService is now processing
21:15:33.794 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.business.delegate.YouTubeService - YouTubeService is now processingWhen to Use the Business Delegate Pattern in Java
Use the Business Delegate pattern when
- You need loose coupling between presentation and business tiers or need to abstract service lookups.
- You want to orchestrate calls to multiple business services
- You want to encapsulate service lookups and service calls
- There is a need to abstract and encapsulate the communication between the client tier and business services
Business Delegate Pattern Java Tutorials
Real-World Applications of Business Delegate Pattern in Java
- Enterprise applications using Java EE (Java Platform, Enterprise Edition)
- Applications requiring remote access to business services
Benefits and Trade-offs of Business Delegate Pattern
Benefits:
- Decoupling of Presentation and Business Tiers: Allows the client tier and business services to evolve independently.
- Location Transparency: Clients remain unaffected by changes in the location or the instantiation of business services.
- Reuse and Scalability: Business Delegate objects can be reused by multiple clients, and the pattern supports load balancing and scalability.
Trade-offs:
- Complexity: Introduces additional layers and abstractions, which may increase complexity.
- Performance Overhead: The additional indirection may incur a slight performance penalty.
Related Java Design Patterns
- Service Locator: Business Delegate uses Service Locator to locate business services.
- Session Facade: Business Delegate may use Session Facade to provide a unified interface to a set of business services.
- Composite Entity: Business Delegate may use Composite Entity to manage the state of business services.