Naked Objects Pattern in Java: Leveraging Domain Objects for Dynamic UI Generation
Also known as
- Transparent Objects
Intent of Naked Objects Design Pattern
To enable the rapid development of maintainable systems by representing all business objects directly and automatically creating the user interface from these definitions. Naked Objects design pattern is essential for developers aiming to align user interfaces with domain models seamlessly.
Detailed Explanation of Naked Objects Pattern with Real-World Examples
Real-world example
In a Naked Objects design pattern, a company might develop a customer relationship management (CRM) system where each business object, such as "Customer," "Order," and "Product," is represented directly. This allows for a dynamic and adaptable UI reflecting the underlying domain model with minimal developer intervention. The user interface is automatically generated based on these domain objects, allowing sales representatives to view and edit customer information, track orders, and manage inventory without needing a separately designed UI.
This approach ensures that any changes in the business logic or domain model are immediately reflected in the user interface, significantly reducing the development and maintenance time. For instance, if a new field, "Loyalty Points," is added to the "Customer" object to track rewards, this field automatically appears in the CRM's user interface without additional UI development. This keeps the system flexible and closely aligned with the evolving business needs.
In plain words
The Naked Objects design pattern automatically generates a user interface from domain objects, allowing for rapid development and easy maintenance by ensuring the UI directly reflects the underlying business model.
Wikipedia says
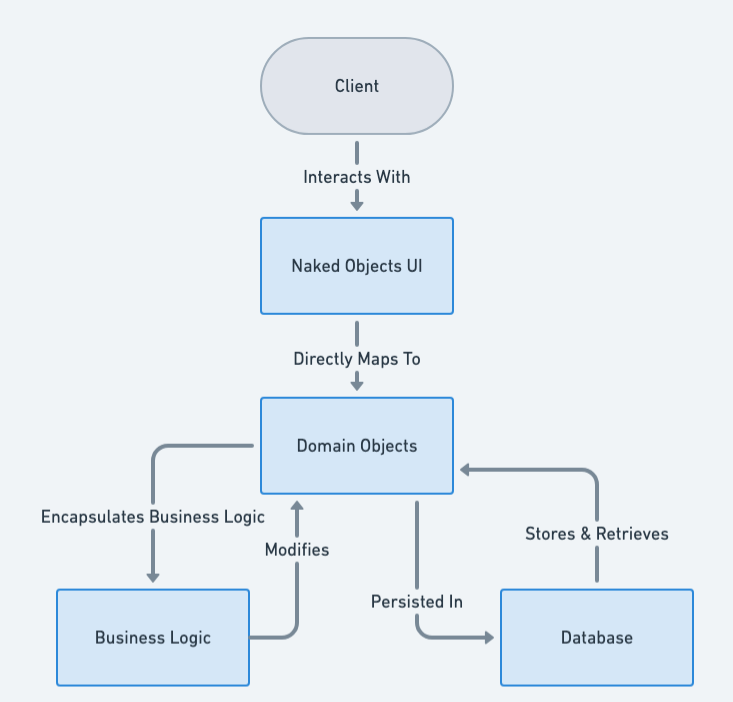
Naked objects is an architectural pattern used in software engineering. It is defined by three principles:
- All business logic should be encapsulated onto the domain objects. This principle is not unique to naked objects; it is a strong commitment to encapsulation.
- The user interface should be a direct representation of the domain objects, with all user actions consisting of creating, retrieving, or invoking methods on domain objects. This principle is not unique to naked objects: it is an interpretation of an object-oriented user interface.
The naked object pattern's innovative feature arises by combining the 1st and 2nd principles into a 3rd principle: 3. The user interface shall be entirely automatically created from the definitions of the domain objects. This may be done using reflection or source code generation.
Architecture diagram
Programmatic Example of Naked Objects Pattern in Java
Consider a simplified example with domain objects representing books and authors. In a Java-based application using the Naked Objects pattern, we define domain objects such as Book and Author. This example illustrates how Naked Objects can streamline user interface generation and domain object manipulation.
Suppose we have the following domain objects in a Java-based application:
@DomainObject
public class Book {
@Property
private String title;
@Property
private String author;
@Action
public void borrow() {
// Implement borrowing logic here
}
}
@DomainObject
public class Author {
@Property
private String name;
@Collection
public List<Book> getBooks() {
// Implement logic to retrieve books by this author
}
@Action
public Book createBook(String title) {
// Implement logic to create a new book by this author
}
}In this example, we define two domain objects: Book and Author. The Book class has properties for the title and author, as well as an action to borrow the book. The Author class has a property for the author's name, a collection of books they have written (getBooks), and an action to create a new book (createBook).
With the Naked Objects framework or tool, the user interface for managing books and authors can be automatically generated based on these domain object definitions. Users can interact with the generated UI to create, retrieve, update, and delete books and authors directly through a user-friendly interface.
Here's how you can use these domain objects to create and interact with books and authors programmatically:
var author = new Author();
author.setName("J.K. Rowling");
var book = author.createBook("Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone");
book.setAuthor(author);
book.borrow();
var booksByAuthor = author.getBooks();This example demonstrates how the Naked Objects pattern can be implemented in a Java-based application with domain objects for books and authors. Users can directly manipulate these domain objects through the generated user interface.
When to Use the Naked Objects Pattern in Java
- When aiming to create a system where the domain objects can be easily understood and manipulated without an explicit user interface design.
- For applications requiring a dynamic, adaptable UI that reflects the underlying domain model with minimal developer intervention.
Real-World Applications of Naked Objects Pattern in Java
- Enterprise applications where business rules and domain logic are primary.
- Systems that benefit from a dynamic and adaptive user interface.
Benefits and Trade-offs of Naked Objects Pattern
Benefits:
- Rapid development
- Improved maintainability
- Easy domain understanding
- Alignment between the UI and business model
Trade-offs:
- Reduced UI flexibility
- Potential over-exposure of the domain model
- Reliance on framework capabilities
Related Java Design Patterns
Active Record: Similar in exposing domain models directly, but Active Record typically involves persistence aspects as well.
Domain-Driven Design: Shares the focus on domain modeling but without the automatic UI generation of Naked Objects.