Observer Pattern in Java: Mastering Reactive Interfaces in Java Applications
Also known as
- Dependents
Intent of Observer Design Pattern
The Observer pattern in Java defines a one-to-many relationship between objects, ensuring that when one object updates its state, all dependent observers are notified and updated automatically, enhancing system responsiveness and modularity.
Detailed Explanation of Observer Pattern with Real-World Examples
Real-world example
In a real-world example, consider a news agency system where the agency (subject) publishes news articles, and multiple news outlets (observers) subscribe to receive updates. Whenever the news agency publishes a new article, it automatically notifies all the subscribed news outlets. These outlets can then update their platforms (like websites, TV broadcasts, or newspapers) with the latest news. This ensures that all subscribers get the latest information without the news agency needing to know the specifics of each outlet's update process. This decouples the news agency from the subscribers, promoting flexibility and modularity in how updates are handled.
In plain words
Implement the Observer interface to actively monitor and respond to state changes in Java applications, improving event-driven programming efficiency.
Wikipedia says
The observer pattern is a software design pattern in which an object, called the subject, maintains a list of its dependents, called observers, and notifies them automatically of any state changes, usually by calling one of their methods.
Sequence diagram
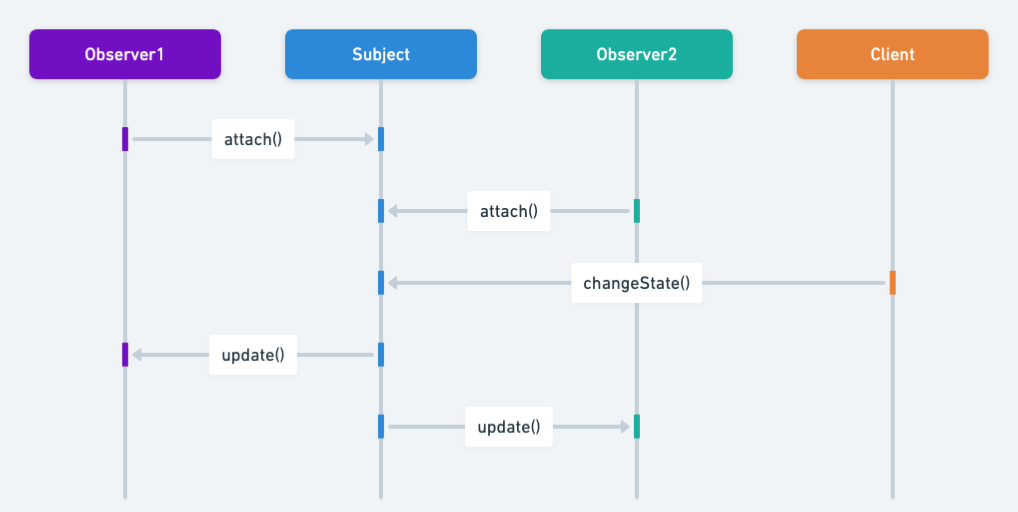
Programmatic Example of Observer Pattern in Java
In a land far away live the races of hobbits and orcs. Both of them are mostly outdoors, so they closely follow the weather changes. One could say that they are constantly observing the weather.
Let's first introduce the WeatherObserver interface and our races, Orcs and Hobbits.
public interface WeatherObserver {
void update(WeatherType currentWeather);
}
@Slf4j
public class Orcs implements WeatherObserver {
@Override
public void update(WeatherType currentWeather) {
LOGGER.info("The orcs are facing " + currentWeather.getDescription() + " weather now");
}
}
@Slf4j
public class Hobbits implements WeatherObserver {
@Override
public void update(WeatherType currentWeather) {
switch (currentWeather) {
LOGGER.info("The hobbits are facing " + currentWeather.getDescription() + " weather now");
}
}
}Then here's the Weather that is constantly changing.
@Slf4j
public class Weather {
private WeatherType currentWeather;
private final List<WeatherObserver> observers;
public Weather() {
observers = new ArrayList<>();
currentWeather = WeatherType.SUNNY;
}
public void addObserver(WeatherObserver obs) {
observers.add(obs);
}
public void removeObserver(WeatherObserver obs) {
observers.remove(obs);
}
/**
* Makes time pass for weather.
*/
public void timePasses() {
var enumValues = WeatherType.values();
currentWeather = enumValues[(currentWeather.ordinal() + 1) % enumValues.length];
LOGGER.info("The weather changed to {}.", currentWeather);
notifyObservers();
}
private void notifyObservers() {
for (var obs : observers) {
obs.update(currentWeather);
}
}
}Here's the full example in action.
public static void main(String[] args) {
var weather = new Weather();
weather.addObserver(new Orcs());
weather.addObserver(new Hobbits());
weather.timePasses();
weather.timePasses();
weather.timePasses();
weather.timePasses();
// Generic observer inspired by Java Generics and Collections by Naftalin & Wadler
LOGGER.info("--Running generic version--");
var genericWeather = new GenWeather();
genericWeather.addObserver(new GenOrcs());
genericWeather.addObserver(new GenHobbits());
genericWeather.timePasses();
genericWeather.timePasses();
genericWeather.timePasses();
genericWeather.timePasses();
}Program output:
21:28:08.310 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Weather -- The weather changed to rainy.
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Orcs -- The orcs are facing Rainy weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Hobbits -- The hobbits are facing Rainy weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Weather -- The weather changed to windy.
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Orcs -- The orcs are facing Windy weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Hobbits -- The hobbits are facing Windy weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Weather -- The weather changed to cold.
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Orcs -- The orcs are facing Cold weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Hobbits -- The hobbits are facing Cold weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Weather -- The weather changed to sunny.
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Orcs -- The orcs are facing Sunny weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.Hobbits -- The hobbits are facing Sunny weather now
21:28:08.312 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.App -- --Running generic version--
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenWeather -- The weather changed to rainy.
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenOrcs -- The orcs are facing Rainy weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenHobbits -- The hobbits are facing Rainy weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenWeather -- The weather changed to windy.
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenOrcs -- The orcs are facing Windy weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenHobbits -- The hobbits are facing Windy weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenWeather -- The weather changed to cold.
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenOrcs -- The orcs are facing Cold weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenHobbits -- The hobbits are facing Cold weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenWeather -- The weather changed to sunny.
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenOrcs -- The orcs are facing Sunny weather now
21:28:08.313 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.observer.generic.GenHobbits -- The hobbits are facing Sunny weather nowWhen to Use the Observer Pattern in Java
Use the Observer pattern in any of the following situations:
- When an abstraction has two aspects, one dependent on the other. Encapsulating these aspects in separate objects lets you vary and reuse them independently.
- When a change to one object requires changing others, and you don't know how many objects need to be changed.
- When an object should be able to notify other objects without making assumptions about who these objects are. In other words, you don't want these objects tightly coupled.
Real-World Applications of Observer Pattern in Java
- java.util.Observer
- java.util.EventListener
- javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener
- RxJava
- Model-View-Controller (MVC) frameworks.
- Event handling systems.
Benefits and Trade-offs of Observer Pattern
Benefits:
- This Java design pattern promotes loose coupling, allowing the subject and its observers to interact without tight dependencies, facilitating easier maintenance and scalability.
- Allows dynamic subscription and unsubscription of observers.
Trade-offs:
- Can lead to memory leaks if observers are not properly deregistered.
- The order of notification is not specified, leading to potential unexpected behavior.
- Potential for performance issues with a large number of observers.
Related Java Design Patterns
- Mediator: Encapsulates how a set of objects interact, which can be used to reduce the direct dependencies among objects.
- Singleton: Often used with the Observer pattern to ensure a single instance of the subject.