Bridge
大约 3 分钟
又被称为
手柄/身体模式
目的
将抽象与其实现分离,以便二者可以独立变化。
解释
真实世界例子
考虑一下你拥有一种具有不同附魔的武器,并且应该允许将具有不同附魔的不同武器混合使用。 你会怎么做? 为每个附魔创建每种武器的多个副本,还是只是创建单独的附魔并根据需要为武器设置它? 桥接模式使您可以进行第二次操作。
通俗的说
桥接模式是一个更推荐组合而不是继承的模式。将实现细节从一个层次结构推送到具有单独层次结构的另一个对象。
维基百科说
桥接模式是软件工程中使用的一种设计模式,旨在“将抽象与其实现分离,从而使两者可以独立变化”
程序示例
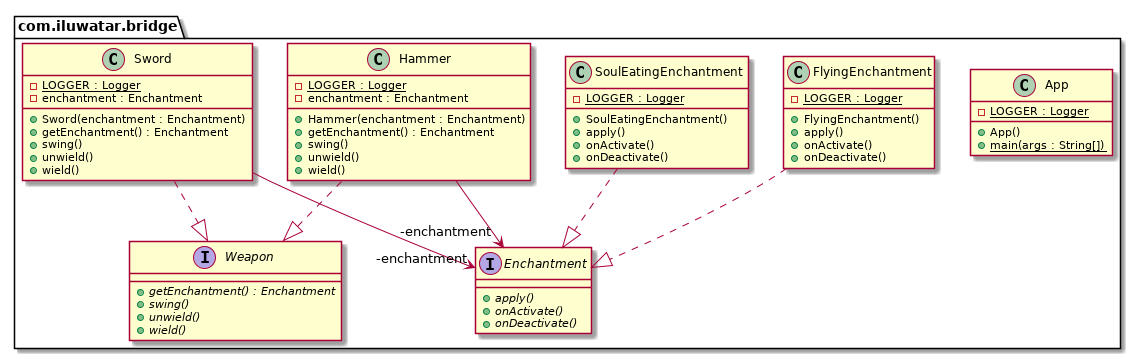
翻译一下上面的武器示例。下面我们有武器的类层级:
public interface Weapon {
void wield();
void swing();
void unwield();
Enchantment getEnchantment();
}
public class Sword implements Weapon {
private final Enchantment enchantment;
public Sword(Enchantment enchantment) {
this.enchantment = enchantment;
}
@Override
public void wield() {
LOGGER.info("The sword is wielded.");
enchantment.onActivate();
}
@Override
public void swing() {
LOGGER.info("The sword is swinged.");
enchantment.apply();
}
@Override
public void unwield() {
LOGGER.info("The sword is unwielded.");
enchantment.onDeactivate();
}
@Override
public Enchantment getEnchantment() {
return enchantment;
}
}
public class Hammer implements Weapon {
private final Enchantment enchantment;
public Hammer(Enchantment enchantment) {
this.enchantment = enchantment;
}
@Override
public void wield() {
LOGGER.info("The hammer is wielded.");
enchantment.onActivate();
}
@Override
public void swing() {
LOGGER.info("The hammer is swinged.");
enchantment.apply();
}
@Override
public void unwield() {
LOGGER.info("The hammer is unwielded.");
enchantment.onDeactivate();
}
@Override
public Enchantment getEnchantment() {
return enchantment;
}
}这里是单独的附魔类结构:
public interface Enchantment {
void onActivate();
void apply();
void onDeactivate();
}
public class FlyingEnchantment implements Enchantment {
@Override
public void onActivate() {
LOGGER.info("The item begins to glow faintly.");
}
@Override
public void apply() {
LOGGER.info("The item flies and strikes the enemies finally returning to owner's hand.");
}
@Override
public void onDeactivate() {
LOGGER.info("The item's glow fades.");
}
}
public class SoulEatingEnchantment implements Enchantment {
@Override
public void onActivate() {
LOGGER.info("The item spreads bloodlust.");
}
@Override
public void apply() {
LOGGER.info("The item eats the soul of enemies.");
}
@Override
public void onDeactivate() {
LOGGER.info("Bloodlust slowly disappears.");
}
}这里是两种层次结构的实践:
var enchantedSword = new Sword(new SoulEatingEnchantment());
enchantedSword.wield();
enchantedSword.swing();
enchantedSword.unwield();
// The sword is wielded.
// The item spreads bloodlust.
// The sword is swinged.
// The item eats the soul of enemies.
// The sword is unwielded.
// Bloodlust slowly disappears.
var hammer = new Hammer(new FlyingEnchantment());
hammer.wield();
hammer.swing();
hammer.unwield();
// The hammer is wielded.
// The item begins to glow faintly.
// The hammer is swinged.
// The item flies and strikes the enemies finally returning to owner's hand.
// The hammer is unwielded.
// The item's glow fades.类图
适用性
使用桥接模式当
- 你想永久性的避免抽象和他的实现之间的绑定。有可能是这种情况,当实现需要被选择或者在运行时切换。
- 抽象和他们的实现应该能通过写子类来扩展。这种情况下,桥接模式让你可以组合不同的抽象和实现并独立的扩展他们。
- 对抽象的实现的改动应当不会对客户产生影响;也就是说,他们的代码不必重新编译。
- 你有种类繁多的类。这样的类层次结构表明需要将一个对象分为两部分。Rumbaugh 使用术语“嵌套归纳”来指代这种类层次结构。
- 你想在多个对象间分享一种实现(可能使用引用计数),这个事实应该对客户隐藏。一个简单的示例是Coplien的String类,其中多个对象可以共享同一字符串表示形式