Service to Worker Pattern in Java: Enhancing UI and Business Logic Integration
Intent of Service to Worker Design Pattern
The Service to Worker design pattern in Java combines the Dispatcher View and Service Locator patterns to facilitate the separation of processing, control flow, and view management in web applications.
Detailed Explanation of Service to Worker Pattern with Real-World Examples
Real-world example
Imagine a large restaurant chain with a central kitchen and multiple waitstaff. When a customer places an order, the waitstaff (Controller) takes the order and hands it over to the kitchen (Service). The kitchen then processes the order, prepares the dish, and hands it back to the waitstaff. The waitstaff finally delivers the dish to the customer (View). This scenario mirrors Java web applications using the Service to Worker pattern, where backend logic (like the kitchen) is separated from frontend interactions (like the waitstaff), improving focus and efficiency in design pattern implementation.
In plain words
Separates the processing logic from the view in web applications to improve maintainability and scalability.
Sequence diagram
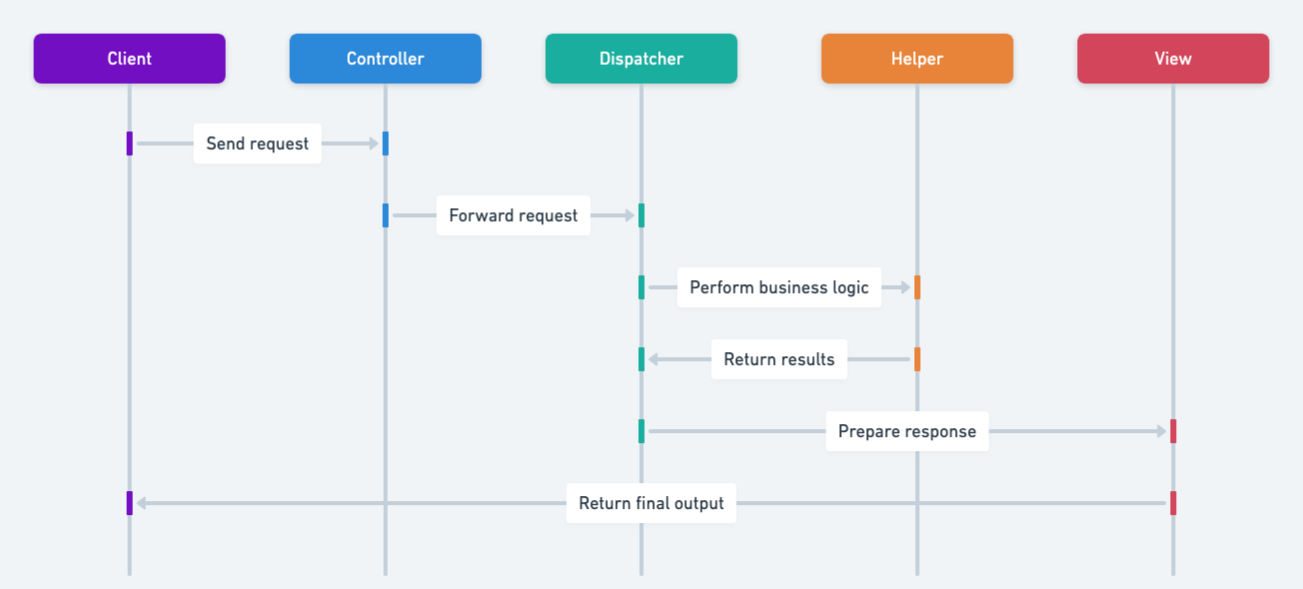
Programmatic Example of Service to Worker Pattern in Java
The Service to Worker design pattern separates the processing logic from the view in web applications to improve maintainability and scalability. It combines the Dispatcher View and Service Locator patterns to facilitate the separation of processing, control flow, and view management in web applications.
In our example, we have a GiantController class, which acts as the controller in the Service to Worker pattern. It takes commands and updates the view. The Dispatcher class is responsible for performing actions and updating the view.
Here is the GiantController class:
public class GiantController {
public Dispatcher dispatcher;
public GiantController(Dispatcher dispatcher) {
this.dispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public void setCommand(Command s, int index) {
dispatcher.performAction(s, index);
}
public void updateView(GiantModel giantModel) {
dispatcher.updateView(giantModel);
}
}In the GiantController class, we have a setCommand method that takes a Command and an index. This method is used to control the dispatcher. The updateView method is used to update the view with the provided GiantModel.
The App class is the entry point of our application:
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var giant1 = new GiantModel("giant1", Health.HEALTHY, Fatigue.ALERT, Nourishment.SATURATED);
var giant2 = new GiantModel("giant2", Health.DEAD, Fatigue.SLEEPING, Nourishment.STARVING);
var action1 = new Action(giant1);
var action2 = new Action(giant2);
var view = new GiantView();
var dispatcher = new Dispatcher(view);
dispatcher.addAction(action1);
dispatcher.addAction(action2);
var controller = new GiantController(dispatcher);
controller.updateView(giant1);
controller.updateView(giant2);
controller.setCommand(new Command(Fatigue.SLEEPING, Health.HEALTHY, Nourishment.STARVING), 0);
controller.setCommand(new Command(Fatigue.ALERT, Health.HEALTHY, Nourishment.HUNGRY), 1);
controller.updateView(giant1);
controller.updateView(giant2);
}
}In the main method, we create two GiantModel instances, giant1 and giant2, and two Action instances, action1 and action2. We then create a GiantView instance and a Dispatcher instance. We add action1 and action2 to the Dispatcher and create a GiantController with the Dispatcher. We then update the view with giant1 and giant2, set some commands, and update the view again.
Console output:
12:23:10.895 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.servicetoworker.GiantView -- Giant giant1, The giant looks healthy, alert and saturated.
12:23:10.897 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.servicetoworker.GiantView -- Giant giant2, The giant looks dead, sleeping and starving.
12:23:10.897 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.servicetoworker.GiantView -- Giant giant1, The giant looks healthy, sleeping and starving.
12:23:10.897 [main] INFO com.iluwatar.servicetoworker.GiantView -- Giant giant2, The giant looks healthy, alert and hungry.This is a simple example of how the Service to Worker pattern can be implemented in a Java application.
When to Use the Service to Worker Pattern in Java
- Use when you need to separate the controller logic from the view to improve code maintainability and enable team members to work on different parts of the application independently.
- Suitable for Java web applications that utilize MVC architecture.
- Appropriate for scenarios requiring complex request processing before displaying a view.
Real-World Applications of Service to Worker Pattern in Java
- Java-based web frameworks like Struts and Spring MVC.
- Enterprise web applications requiring a clean separation between presentation logic and business logic.
Benefits and Trade-offs of Service to Worker Pattern
Benefits:
- Enhances code maintainability by separating concerns.
- Facilitates team collaboration by decoupling the controller and view components.
- Simplifies the addition of new views and modifications to existing ones.
Trade-offs:
- Increases the complexity of the application structure.
- May introduce additional overhead due to the layered architecture.
Related Java Design Patterns
- Model-View-Controller (MVC): Service to Worker is a specialized form of MVC, focusing on separating request handling and view management.
- Front Controller: Often used in conjunction with Service to Worker to centralize request handling and routing.